Atopic Dermatitis
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a long-lasting skin disease and it is commonly known as atopic eczema. The word “atopic” refers to a predisposition some people seem to have to develop dermatitis along with asthma and/or hay fever, allergic rhinitis, which is referred to as “atopy”
What causes it?
The cause of atopic dermatitis is a combination of genetic, immune and environmental factors.
Despite popular belief, eczema is NOT linked to any type of food allergy.Some factors can make your eczema worse, for example
- Heat, sweating
- Dry environment, cold season
- Emotional stress or anxiety
- Rapid temperature changes
- Exposure to certain chemicals or cleaning solutions, including soaps and detergents, perfumes and cosmetics.
- Clothing made of fibres or wool
- Exposure to dust, sand and cigarette smoke
- Scratching
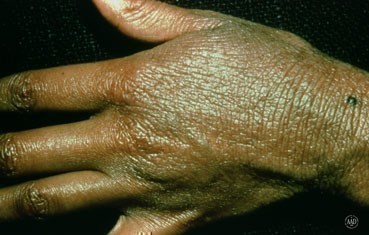
How does it Manifest?
Atopic dermatitis is the most common of the many types of eczema. The onset typically begins in childhood and can last through adulthood.
It can be different in each person, for example
- You might feel your skin is very itchy, and becomes more itchy at night
- You might notice some small raised bumps sometimes filled with fluid on the hands and/or feet.
- There might be red patches on your skin scattered on different parts of the body. Babies may have these patches on the face and scalp too.
- If it has been there for a long time, your skin can feel thickened, dry and flacky
- Scratching lead to swelling, cracking and sometimes fluid oozing from the skin. All this makes the skin sensitive.
- All these makes it easy for the skin to be infected.
What measures can I take?
- Avoid things that make your eczema to flare.
- Wear cotton clothing
- Use mild, moisturizing soap and avoid hot water. Pad your skin dry with a soft towel and then apply lotions whilst your skin is still damp.
- Avoid scratching the irritated area since it can make the rash worse.
- Avoid too much heat and sweaty.
- Learn how to cope with stress. Avoid triggering stressful situations.
What treatment can help me?
- Always keep you skin well moisturized. Health professionals can suggest what emollients to use.
- Your doctor will tell you what is best for and how to use steroid creams/ointments.
- There are different ways of how to treat your eczema depending on the severity. Visit your doctor if you are not coping at home.
- Control your itching. If you are having trouble sleeping because of the itching, your doctor might recommend an antihistamine that can help with sleep. Sometimes wet wraps can be recommended.
